Many have been said about Ecuador´s biodiversity and its four worlds or regions: The Amazonia, the Andes, the Pacific Coast, and the Galapagos Islands. Each one of them has unique biodiversity in an array of ecosystems. But do you know why Ecuador´s flora and fauna are crucial to the Earth?
Now it’s time to talk about it and enchant you with the uniqueness of a country with an equivalent size around the size of Nevada in the US, or 20% bigger than the UK.
Keep reading and discover why Ecuador is so megadiverse.
What does megadiverse mean?
According to Biodiversity A-Z, megadiversity refers to the world’s top biodiversity-rich nations. This approach is country-specific and aims to increase national awareness of the need to conserve biodiversity in countries with a high level of biological variety and many endemic species.

This categorization highlights how a few nations have a substantial part of global diversity and bear the responsibility for conservation and biodiversity management.
Did you know that there are only 17 megadiverse countries worldwide?
Indeed, Ecuador is among Colombia, Peru, Venezuela, and Brazil as megadiverse countries in South America. That’s because our planet’s biodiversity distribution is not uniform, and some regions—particularly those in the tropics—have far higher concentrations of species than others.
We invite you to watch the following video explaining this concept and each country’s characteristics (don’t forget to turn on the CC in English).
Why is Ecuador so biodiverse?
As we mentioned previously, tropical countries have a higher concentration of species, and Ecuador is in the middle of the world, and that’s why there are confluences in the warm northern currents and the cold southern winds and water currents.
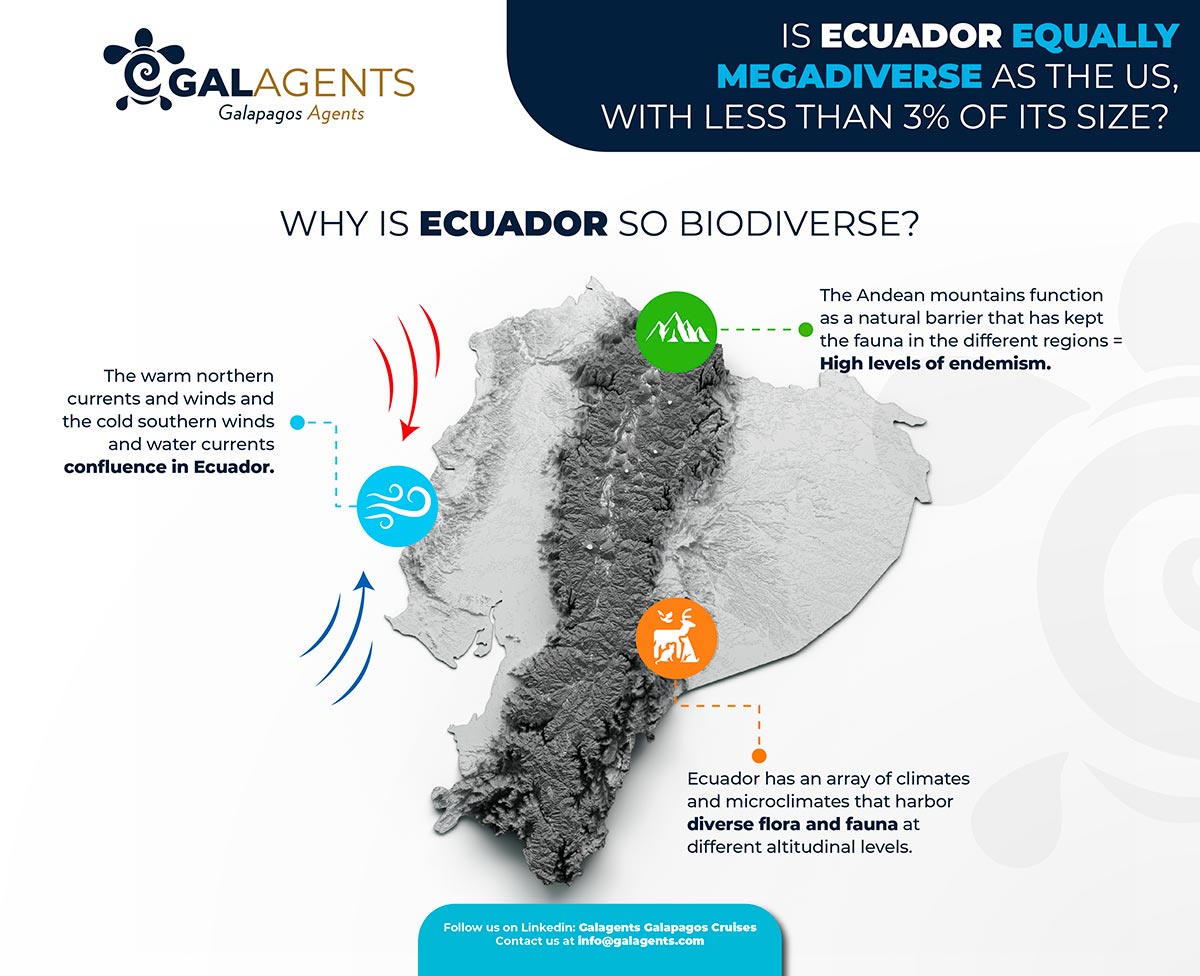
The Andean mountains function as a natural barrier that has kept the fauna in the different regions, which has helped to get high levels of endemism.
Ecuador’s different altitudinal levels are another fact of its biodiversity because it has an array of climates and microclimates that harbor diverse flora and fauna. Also, climates function as a natural border for some species that live in specific weather conditions.
Seven biosphere reserves in one country
The United Nations developed the Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) in the early 1970s to encourage sustainable development. Since then, there has been a network of biosphere reserves worldwide to provide a functional, balanced interaction between humans and the natural environment.
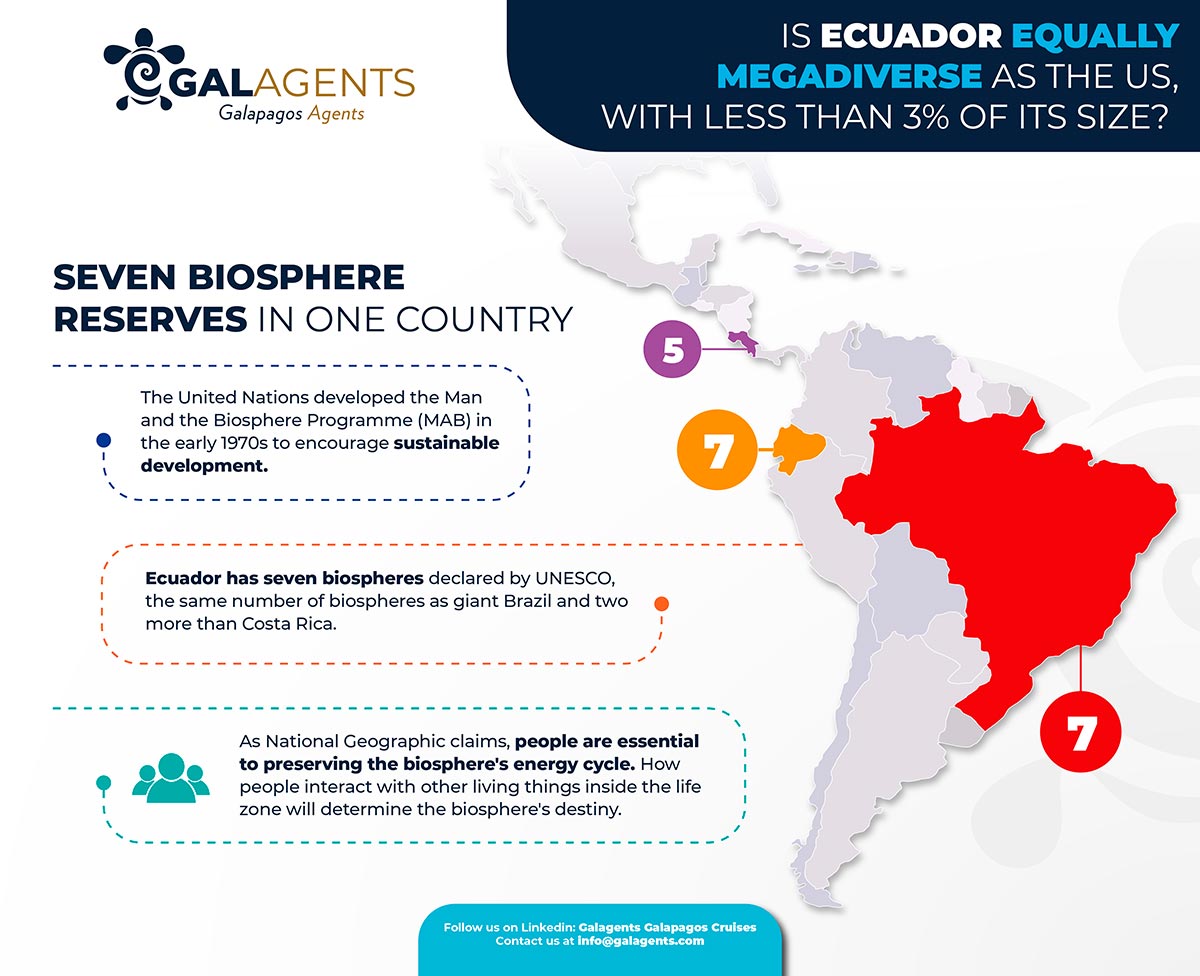
Ecuador has seven biospheres declared by UNESCO, and the newest one is the Andean Chocó Forest proclaimed in 2018. Surprisingly, tiny Ecuador has the same number of biospheres as giant Brazil and two more than Costa Rica, considered a green and natural destination by excellence worldwide.
As National Geographic claims, people are essential to preserving the biosphere’s energy cycle. However, occasionally, people obstruct the flow. For instance, when people cut forests or burn fossil fuels like coal and oil, the amounts of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere change. Industrial waste and oil spills pose a hazard to hydrosphere life. How people interact with other living things inside the life zone will determine the biosphere’s destiny.
Which are the biospheres of Ecuador?
- The Galapagos Islands were declared in 1984 due to its endemic and unique native flora and fauna, making this archipelago one of the world’s genuinely exceptional places.
- The Yasuní Rainforest, declared in 1989, has some of the most biodiversity per square meter on the earth, where the original natural vegetation covers 99.73% of the biosphere reserve.
- The Sumaco declared in 2000, has numerous watercourses in the area (Napo and Pichincha), and covers a large variety of ecosystems from the tropical highlands-Andean paramour to the tropical Amazon plains.

Download all the infographics here
- The Podocarpus – El Condor was declared in 2007. This Biosphere Reserve is one of the areas with the most remarkable biological diversity in the Neotropics, covering three national protected areas: Podocarpus National Park, Yacuri National Park, and Cerro Plateado Biological Reserve.
- Macizo del Cajas, declared in 2013, has many ecosystems ranging from high mountains down to coastal and marine areas along the Pacific. It plays a vital role in water provision and regulation.
- The Ecuador Dry Forest, designated in 2017, was the 1st transboundary biosphere reserve established in South America between Ecuador and Peru. It has a high degree of endemism, and the seasonally dry forests of Ecuador and Peru, which form the heart of the Endemic Region of Tumbes, one of the most important biodiversity hotspots of the world, as well as the mangroves of Tumbes.
- The Andean Chocó, declared in 2018 at Pichincha Province, is as biodiverse as the Amazon and Galapagos, with high endemism levels. The Chocó Andino region extends over two critical ecoregions: the humid forest lowlands of the Chocó – Darien, which extend from Panama to the Ecuadorian West, and the Northern Andean Mountain Forests.
Up to this point, you may have caught why Ecuador is a nature destination for nature lovers. From the famous Galapagos Islands to the Amazon, the Andes, and the Coast, Ecuador is a paradise for those travelers interested in nature and ecotourism. If you want that we talk more about one specific region based on these Biospheres, let us know in the comments.
And, to answer our main question, Ecuador has seven biospheres. At the same time, the US also has seven biosphere reserves in a territory 35 times bigger than tiny Ecuador, and the following video showcases its biodiversity.

